COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








Need computing power or storage space? AWS has it.
Want to deliver content quickly around the world? AWS can do that, too.
Looking for ways to use artificial intelligence? AWS offers tools for that as well.
This is particularly helpful for startups that might be short on resources or expertise. Instead of worrying about managing servers and complex technical tasks, they can leverage AWS to handle those aspects.
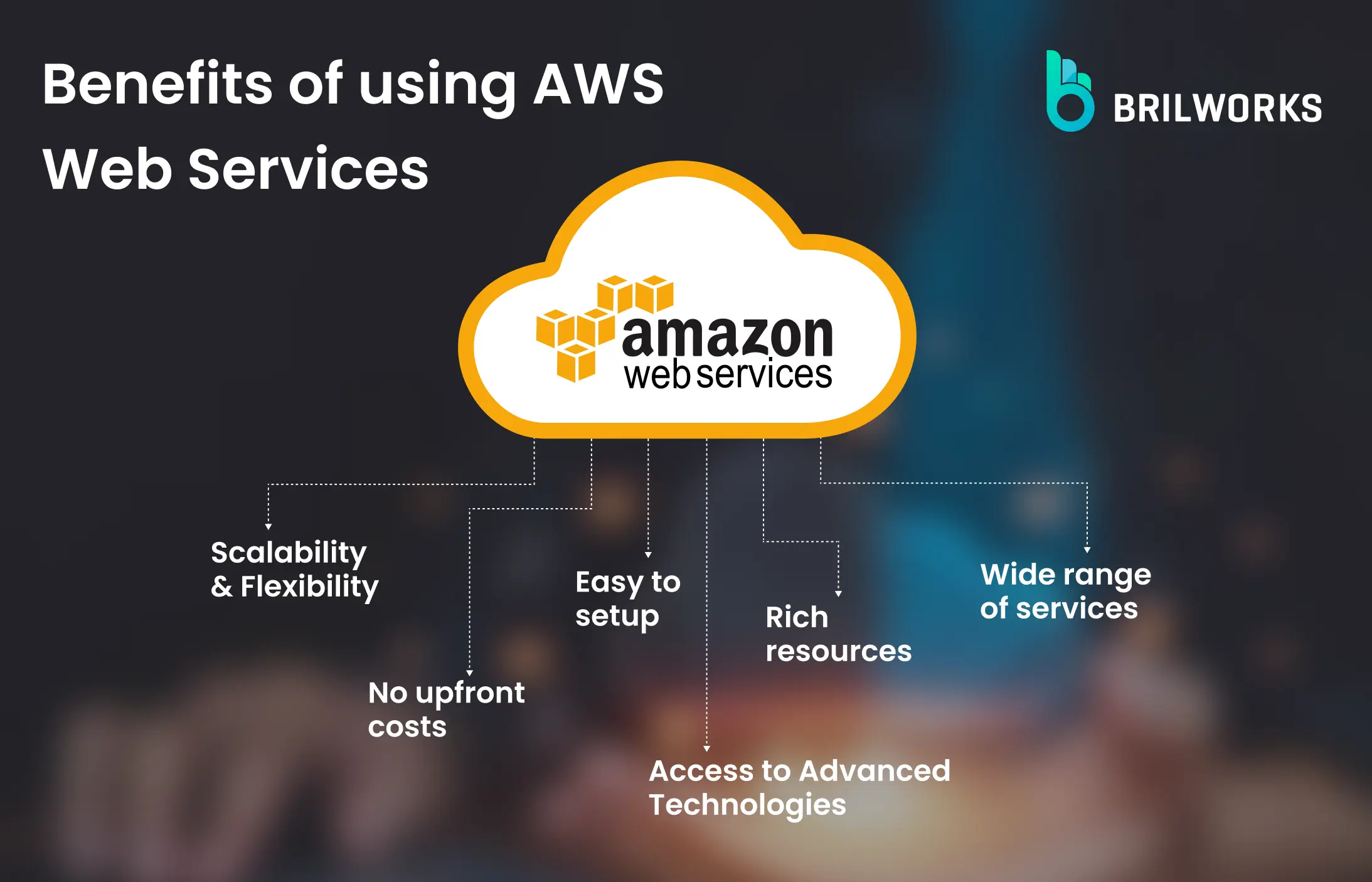
Cloud computing enables businesses to dynamically adjust their resources, such as storage and servers, in response to fluctuating demands without the need for costly physical upgrades.
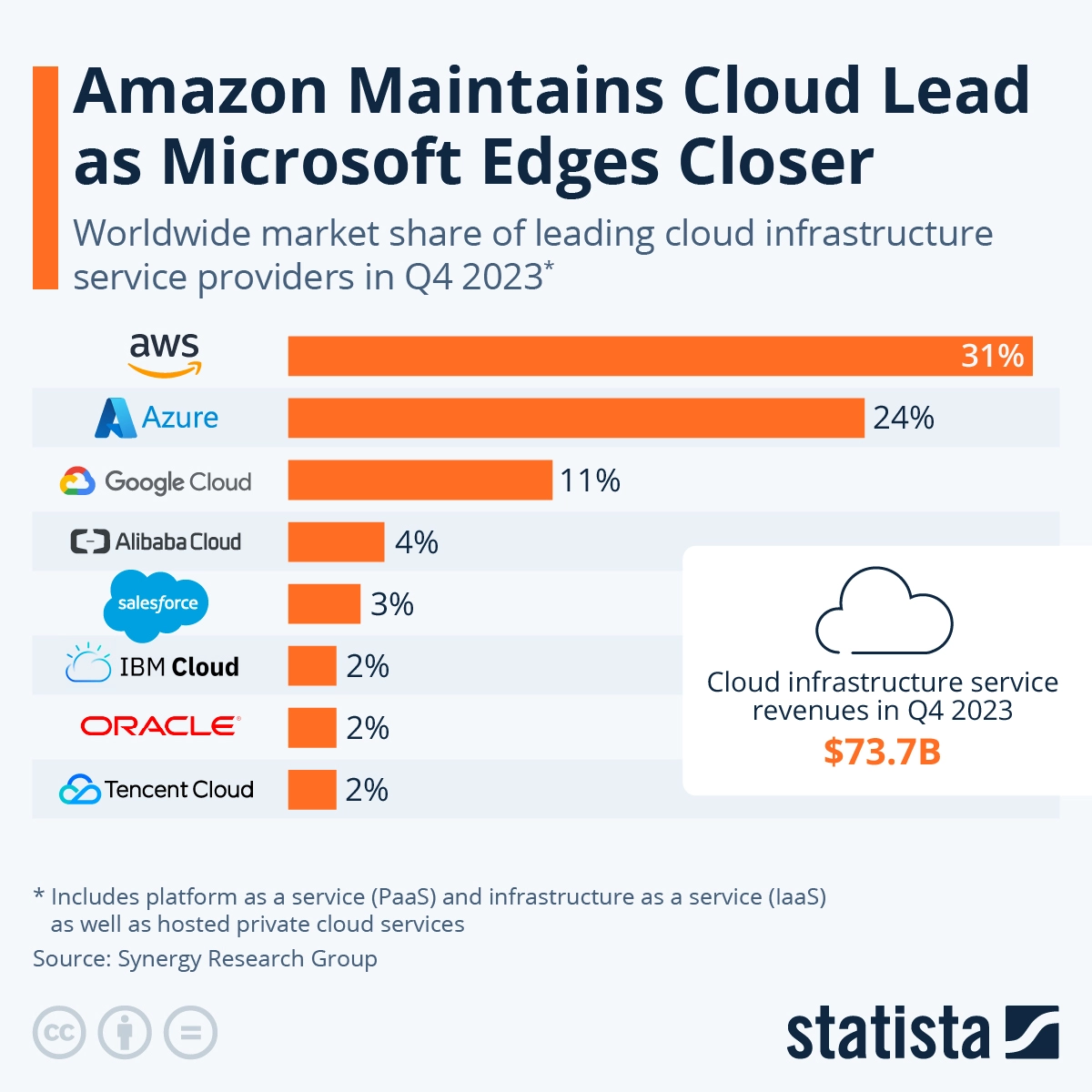
One prominent provider in this space is Amazon Web Services (AWS), which holds over 30% of the global cloud market share. In this article, we will explore AWS services and how they benefit businesses.
Whether you're just beginning your exploration of cloud infrastructure or considering a transition to the cloud, understanding AWS and its offerings is essential. This guide is tailored for beginners.
AWS stands for Amazon Web Services, which encompasses an array of IT infrastructure and services.
In other words, it is a comprehensive suite of cloud services by Amazon that includes over 300 solutions for everything a business or individual may need, including computing, storage, databases, analytics, and much more. While AWS primarily targets businesses, individuals can also leverage its services.
It includes a vast array of services, which include:
Virtual machines, serverless computing, container orchestration (like Kubernetes)
Relational, NoSQL, and other database solutions
Building and managing virtual networks, firewalls, and load balancers
Big data processing, machine learning, and data warehousing services
Identity and access management, encryption, and other security tools
These services are used to deploy, develop, and manage complex applications.
You can think of AWS as a virtual utility:
You access computing power, storage, databases, and other IT resources, all accessible via the Internet. – on-demand and scalable. This eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own physical infrastructure.
To better understand AWS, you need to understand the terms SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
AWS or AWS cloud servcies frees you from the hassle of purchasing and upkeeping your own physical equipment (servers, storage). Instead, you rent them online from a provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS provides various tiers of service within this cloud environment.
The service provider offers virtual machines (like powerful computers), storage space, and networking.
It includes the tools and platform you need to build specific things.
The service provider offers software applications (like email or photo editing) that you can access directly through the cloud without needing to build or maintain them yourself.
AWS primarily focuses on IaaS, offering the building blocks (virtual machines, storage) for businesses to develop their own tools and applications.
Simply put, if you need things like smart AI, lots of computer power, space to store data, or help delivering content online, AWS has what you need. With AWS, you can make complex applications that are flexible, can grow as you need them to, and work reliably.
AWS is trusted by millions of businesses, from small startups to big companies and even government agencies, as it is a reliable, secure, and highly scalable platform.
AWS customers mainly involve startups and small—and medium-sized businesses, with over millions of active customers. It helps businesses by providing them with a robust and highly scalable foundation on which they can scale as much as they want.
In addition, many businesses use it when they lack the expertise to set up hardware for compute and server infrastructure.
AWS shines in both cases. We cannot ignore that it offers a powerful layer of security. Infrastructure setups and security enhancements are major concerns for businesses of all sizes worldwide.
AWS platform acts as an infrastructure that can be scaled according to usage based on your requirements. During peak traffic, it can automatically scale itself, and when demand subsides, auto-scaling can remove unnecessary resources.
Beginners often lack the capital to invest in expensive servers and infrastructure. AWS significantly reduces the upfront investment. Its pay-as-you-go model ensures beginners only pay for the resources they use, making it an affordable way to experiment and learn.
The in-house setup might not be easy for many businesses. And when you looking for easy to use platform without a team, AWS can be viable platform that can be run in a moment. It has an array of services that can be easily deployed and used. For example: Pre-configured services like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) that provides virtual servers ready to use within minutes. This eliminates the burden of server management and allows beginners to focus on development and deployment.
Beginners might not have the expertise or resources to leverage sophisticated technologies like Machine Learning (ML) or Artificial Intelligence (AI). AWS offers a wide range of pre-built services like Amazon SageMaker, enabling beginners to experiment with AI/ML without the need for extensive technical knowledge. This opens doors to exploring advanced functionalities within their applications.
AWS offers a free tier that provides access to a limited set of services for a specific period. This allows beginners to experiment, build basic applications, and get familiar with the platform without incurring any charges. Additionally, AWS provides a vast library of tutorials, documentation, and online communities specifically designed for beginners to learn and grow their cloud expertise.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services that businesses can leverage to build, deploy, and manage their applications. Below are some of the key AWS services:
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): Provides virtual servers in the cloud, allowing you to scale compute capacity up or down based on your needs.
Amazon Lambda: Serverless compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3): Object storage for all types of data, including archives, websites, and application data.
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS): File storage service for use with EC2 instances.
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS): Managed relational database service supporting various database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
Amazon DynamoDB: NoSQL database service for high performance and scalability.
Amazon Aurora: High-performance, scalable relational database engine compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Create a logically isolated virtual network within the AWS cloud.
Amazon CloudFront: Content Delivery Network (CDN) service for securely delivering content with low latency and high transfer speeds.
Amazon Route 53: Domain Name System (DNS) service for routing internet traffic to your applications.
Amazon Redshift: Data warehousing service for large-scale data analysis.
Amazon QuickSight: Business intelligence service for creating and sharing visualizations of your data.
Amazon Kinesis: Service for real-time data processing and streaming analytics.
Amazon SageMaker: Platform for building, training, and deploying machine learning models.
The AWS Free Tier is an excellent starting point for getting acquainted with AWS, as it provides access to over 100 services and products at no cost. This allows users to explore and experiment with various AWS offerings, run applications, and start building solutions without needing to make any upfront financial commitments.
It's a great way to gain familiarity with the platform and understand its capabilities. For more advanced usage and access to additional features, users may opt to move to the premium tier. This tier provides expanded functionality and support for heavier workloads, serving the needs of businesses and organizations with more demanding requirements.
Selecting the right tier depends on your specific needs and usage patterns. Whether you're an individual developer, a startup, or an enterprise, there's a tier that aligns with your requirements.
It's important to evaluate your usage patterns, anticipated workload, and budget constraints to determine which tier best suits your needs.

If you're considering migrating your business to the AWS cloud or need a comprehensive plan to kickstart your cloud journey, our AWS consultation services are designed to assist you every step of the way. Our services encompass everything from initial planning to deployment, ensuring that you can leverage the AWS platform effectively and efficiently.
Our team of experts will work closely with you to understand your business needs, assess your current infrastructure, and develop a customized strategy tailored to your objectives. We'll guide you through the entire migration process, providing insights, best practices, and hands-on support to ensure a seamless transition to the cloud.
Whether you're looking to optimize your existing cloud environment, implement new solutions, or enhance your overall cloud strategy, our consultation services are here to help. With our expertise and industry-leading knowledge, we'll empower your organization to harness the full potential of AWS and drive innovation for your business.
The AWS Management Console serves as a centralized hub for managing various AWS services and resources. It provides users with a web-based interface that allows them to easily interact with AWS without needing to install any additional software.
Here's a brief overview of its user-friendly interface:
Upon logging in, users are greeted with a customizable dashboard that provides an overview of their AWS environment, including key metrics, recent activities, and recommended services.
The left-hand navigation panel organizes AWS services into categories such as Compute, Storage, Database, Networking, and Management Tools. This makes it easy for users to find and access the specific services they need.
Clicking on a specific service in the navigation panel opens a dedicated page for that service, where users can configure settings, manage resources, and view related information.
The console features a search bar at the top, allowing users to quickly search for specific services, resources, or documentation.
AWS provides wizards and tutorials within the console to guide users through common tasks such as launching an EC2 instance, setting up a database, or configuring a load balancer.
Context-sensitive help is available throughout the console, providing users with relevant information and tips based on their current actions or selections.
Users can customize the console by rearranging dashboard widgets, pinning frequently accessed services, and setting preferences according to their workflow.
Overall, the AWS Management Console offers a user-friendly interface that simplifies the process of managing and interacting with AWS services, making it accessible to both beginners and experienced users alike.
Leading enterprises such as Netflix, Amazon, Spotify, Airbnb, Twitch, and X (formerly Twitter) rely on the AWS platform as the backbone of their operations. With a commanding 31% market share in the cloud segment, AWS enables millions of businesses and individuals to scale their operations and develop applications that might not be feasible with in-house infrastructure.
The most common applications of AWS are storage and backup, big data, mobile, social networking, AI, and website development. Below are some popular applications of the AWS platform.
AWS is majorly used as a storage and backup solution for a large database, providing you with different kind of storage service to serve the varying needs of the businesses. It provides servies to store structured, unstructured, semi structured, backup and archival data, and big data.
AWS provides scalable and durable storage solutions for businesses to store and back up their data. Amazon S3 offers object storage for storing any type of data, while Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) provides block-level storage volumes for use with EC2 instances. Amazon Glacier is suitable for long-term archival and backup needs.
Many businesses use AWS to host their websites and web applications using services like Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) for virtual servers and Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) for storing static content.
AWS offers a suite of services for processing and analyzing large volumes of data. Amazon Redshift provides data warehousing capabilities for running complex analytics queries, while Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce) allows businesses to process large datasets using Apache Hadoop, Spark, and other big data frameworks.
AWS offers machine learning services that enable businesses to build, train, and deploy machine learning models without requiring expertise in data science or machine learning algorithms. Amazon SageMaker provides a fully managed platform for building, training, and deploying machine learning models at scale.
AWS IoT services enable businesses to connect and manage IoT devices securely at scale. With services like AWS IoT Core, businesses can collect and analyze data from IoT devices to derive insights and automate actions.
AWS provides a suite of tools and services for implementing DevOps practices and automating software development processes. Services like AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeBuild, and AWS CodeDeploy enable businesses to automate code deployment, testing, and monitoring.
Many e-commerce businesses leverage AWS to build and scale their online platforms. AWS provides services like Amazon EC2, Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service), and AWS Lambda for building and running e-commerce applications with high availability and scalability.
AWS offers services for media processing, streaming, and content delivery, making it suitable for media and entertainment businesses. Services like Amazon Elastic Transcoder, Amazon Kinesis Video Streams, and Amazon CloudFront enable businesses to deliver high-quality media content to their audiences.
These are just a few examples of how businesses can leverage AWS to innovate, scale, and drive growth in their respective industries.

In this article, we've offered a beginner's guide to the AWS ecosystem, highlighting its various use cases and advantages to businesses. We have covered the basics of AWS and provided a brief overview of how to get started with the AWS cloud services.
If you're seeking AWS development services, whether it's migrating your business to the cloud, optimizing your existing AWS environment, or hiring a dedicated AWS developer, reach out to us today to begin your journey.
1. What is AWS or AWS compute service?
AWS, short for Amazon Web Services, is a cloud computing platform offered by Amazon. It provides a wide range of cloud services, including computing power, storage, databases, and more, allowing users to build and deploy applications and websites without needing to invest in expensive infrastructure. For beginners in tech, AWS offers an accessible entry point into the world of cloud computing, providing valuable skills that are in high demand in the industry.
2. How does AWS benefit businesses, and what are some common services offered?
AWS offers numerous benefits for businesses, including cost-effectiveness, scalability, reliability, and security. Some common services offered by AWS include Amazon EC2 for virtual servers, Amazon S3 for object storage, Amazon RDS for managed databases, and AWS Lambda for serverless computing. These services empower businesses to innovate rapidly, scale their operations efficiently, and stay competitive in the digital landscape.
3. What are the basic steps to get started with AWS for beginners?
Getting started with AWS is relatively straightforward for beginners. First, create an AWS account to access the platform. Then, familiarize yourself with the AWS Management Console, where you can manage your services and resources. Next, explore AWS's free tier offerings, which allow you to experiment with various services at no cost. Finally, dive into AWS documentation, tutorials, and online courses to learn more about specific services and use cases.
4. How can beginners gain practical experience with AWS?
Beginners can gain practical experience with AWS by working on hands-on projects and labs, such as deploying a static website on Amazon S3, setting up a virtual server on Amazon EC2, or building a serverless application using AWS Lambda. Additionally, participating in AWS certification training programs and joining online communities like the AWS Developer Forums can provide valuable learning opportunities and support from fellow enthusiasts.
How can businesses hire a dedicated AWS developer?
When evaluating candidates, businesses should look for strong knowledge of AWS services, experience with cloud infrastructure and architecture, proficiency in programming languages like Python or Java, and excellent problem-solving and communication skills. Additionally, candidates with AWS certifications and a track record of successful project implementations can be particularly valuable assets to the team.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements