COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








For several decades, Java has been a central technology for enterprises. However, it has emerged as an unrecognized contributor to the cloud era. While newer languages grab headlines, Java remains the backbone for 90% of Fortune 500 companies and 45% of enterprise cloud applications (yes, you read that right). The microservices, Kubernetes, and serverless architectures haven’t sidelined Java; they’ve reinvented it. There are many reasons that large enterprises use Java so heavily.
For one, it is reliable. Second, it is excellent for mission-critical projects. Developers can write front-end or back-end code, which contributes to faster turnaround times for both web and mobile development.
So, why are the leading Java development companies putting so much focus on it for cloud solutions?
The answer is its battle-tested adaptability. Java’s ecosystem has evolved more rapidly than many critics appreciate. With exciting innovations like Quarkus enhancing cloud-native performance, GraalVM’s super-fast startups, and user-friendly frameworks like Spring Boot making microservices easier.
It handles the scaling issues that cloud apps face. It's a mature toolset that can handle whatever gets thrown at it. Moreover, its JVM optimization capabilities provide a lot of value to cloud developers.
Managing cloud infrastructure has its share of challenges. Scalability can be a crucial element. Newer language stacks address this concern, but they have not matured enough to solve all of the problems. Java and its ecosystem offer solid tooling, JVM optimizations, and extensive enterprise refinement. This makes Java a solid language choice for tech leaders who face the scaling complexities of the cloud.
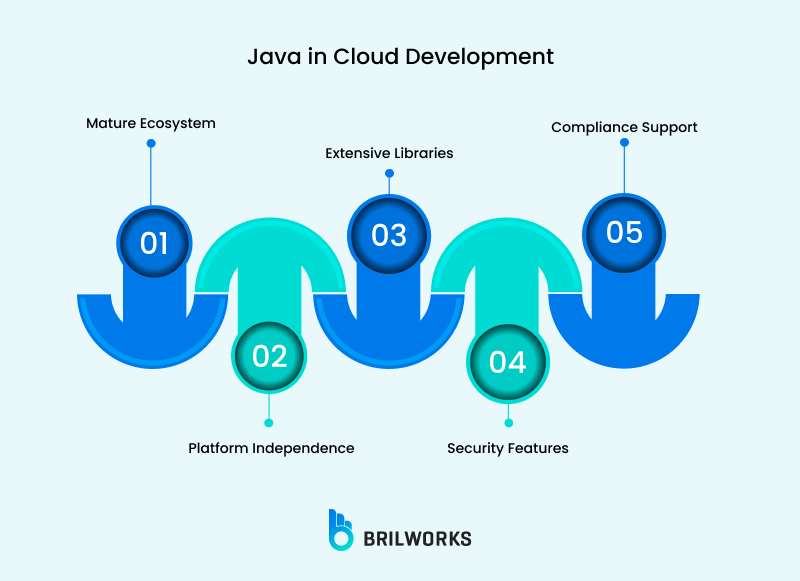
At Brilworks, we've spent a decade turning Java’s “legacy” strengths into cloud-scale advantages. We've seen startups scale to many thousands users on Java-backed Kubernetes clusters and watched enterprises cut cloud costs by 15-30% using JVM tuning most teams overlook.
Having learned what it takes to build a scalable Java application and what best practices to follow in order to build one that can scale over time, let us begin our discussion with Java’s role in cloud computing and examine how it’s performing in today’s cloud-dominated development world.
Seeking to hire Java developers for your next big project? Our seasoned experts are poised to build the robust and scalable applications your business needs. They'll seamlessly integrate with your team, consistently delivering high-performance solutions for even your most ambitious goals.
Predence Research projects a CAGR of 21% for the cloud computing market from 2025 to 2034, with the market reaching approximately $5,150 billion by 2034.
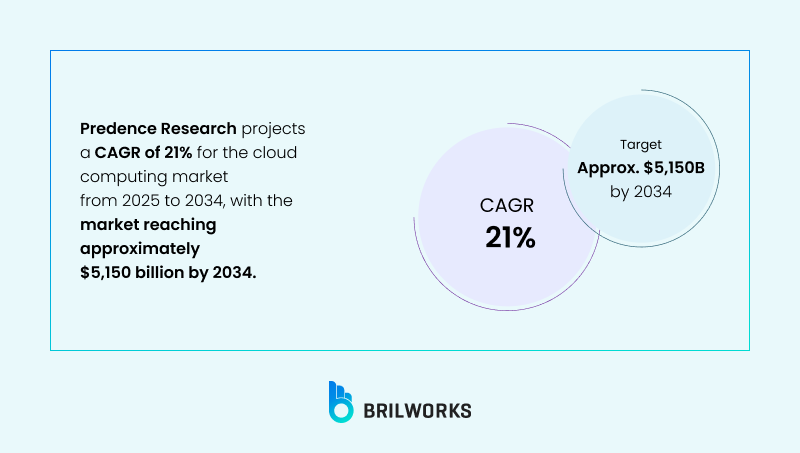
The digital transformation wave continues to grow as more complex apps like AI-powered programs with heavy computations increasingly rely on cloud technologies. So, where does Java fit into all of this?
Cloud migration is on the rise, increasing the need to build, manage, and deploy applications in a language that’s both powerful and adaptive. In the cloud, the best development language for apps that require robust performance, complex workflows, and microservices architecture (for scalability and complex workflows) is arguably Java.
Java is a robust, versatile, and powerful tool, making it a top choice for building mega-enterprise applications. Unfortunately, Java is not cutting it when compared to more modern programming languages. What’s stopping it from keeping up?
In essence, it's the verbosity of the language. However, Kotlin is extending Java’s capabilities and has all the potential to modernize the language. What’s the key takeaway here? It’s vital to understand Java’s place in the modern world, where cloud migration is becoming increasingly popular.
Newer cloud languages like Go and Rust are gaining traction in cloud development. Java’s role in modern cloud development often goes overlooked.
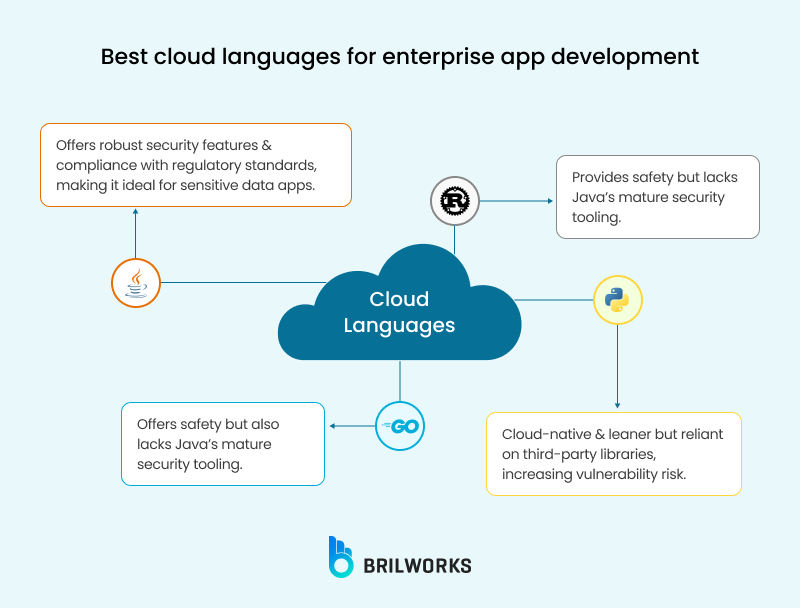
As of 2025, Java is redefining its function through leaner frameworks. It is now ideal for cloud and IoT computing. The language is mature enough to deal with heavy and critical workloads. This is why it has long been a popular choice for creating banking systems and e-commerce platforms.
It now supports Project Loom and virtual threads for extreme concurrency, as well as cloud-native frameworks such as Quarkus and Micronaut to help developers. GraalVM has become prominent in serverless scenarios.
Java isn’t usually the first choice for cloud-native apps, but its ecosystem has come a long way. Today, developers have tools like Micronaut and Quarkus that address some of Java’s traditional challenges, such as slow startup times, high memory usage, and runtime overhead.
Java's platform-agnostic bytecode, in combination with its original slogan "Write once, run anywhere," continues to make cloud environments easier to navigate. When it comes to multi-cloud environments, you can now deploy the exact same app across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, or even your own server with minimal changes to the code itself.
This level of flexibility is a massive plus for programmers. You can, say, port an application developed for Apache Tomcat from an in-house server to an Azure App Service with relatively little effort. It is harder to do that with some other languages.
Java is designed for high-stakes environments. Plus, it has built-in support for encryption, SSL/TLS, and secure key management. These features make Java a strong choice for custom enterprise app development.
Plus, it is one of the top choices for data-sensitive apps, well-suited for building apps that require strict compliance. Its ecosystem aligns with regulatory standards like HIPAA (healthcare) and PCI-DSS (finance).
While languages such as Rust and Go provide safety, they lack Java's mature security tooling. Alternatively, Python and Node.js are cloud-native and leaner, but they are dependent on third-party libraries, which can increase the likelihood of vulnerabilities.
Here are some essential Java security features for cloud development:
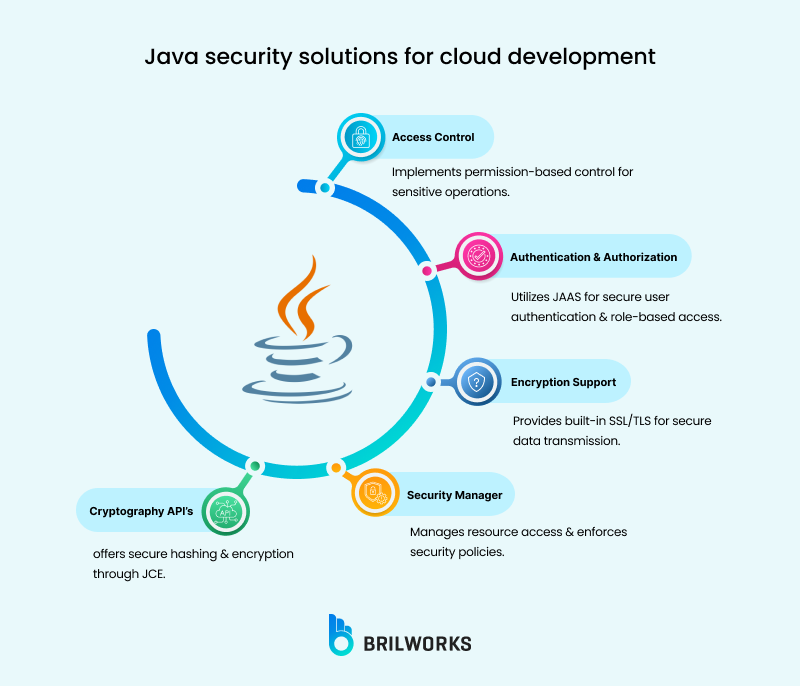
Authentication and Authorization: Uses JAAS (Java Authentication and Authorization Service) for secure user authentication.
Encryption Support: Built-in support for SSL/TLS for secure data transmission.
Security Manager: Controls access to system resources and enforces security policies.
Cryptography APIs: Provides secure hashing and encryption using libraries like JCE (Java Cryptography Extension).
Access Control: Uses permission-based access control for sensitive operations.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL): Supports HTTPS for secure communication between cloud services.
Secure Class Loading: Prevents malicious code from being loaded during runtime.
Sandboxing: Restricts untrusted code from accessing critical resources.
Code Signing: Ensures code integrity and authenticity using digital signatures.
Input Validation: Helps prevent injection attacks and data corruption.
Building a cloud application doesn’t simply depend on choosing a good programming language. It requires choosing the right tools and the right technology to be able to scale it, make sure it is secure, and, more importantly, easy to manage.
Here is a comprehensive guide to everything you need to build a cloud app with Java.
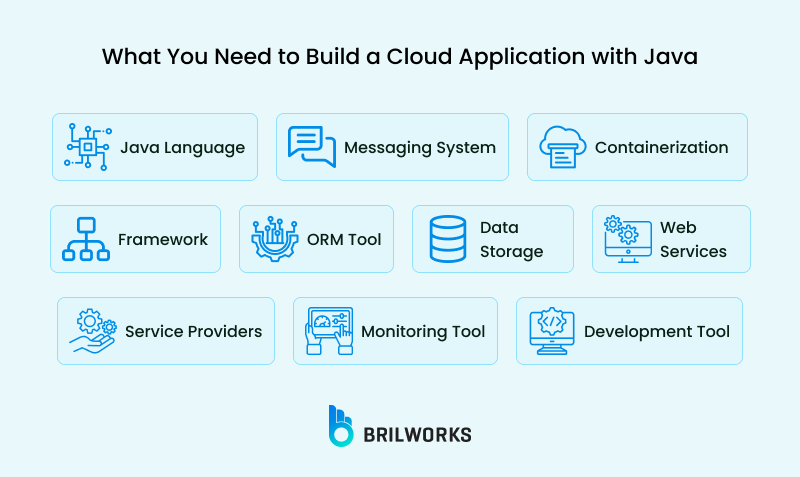
Java is widely used in enterprise environments and is ideal for developing large-scale cloud systems. Moreover, it provides an extensive ecosystem and robust frameworks. This is why it has become one of the go-to choices for building scalable cloud-based applications.
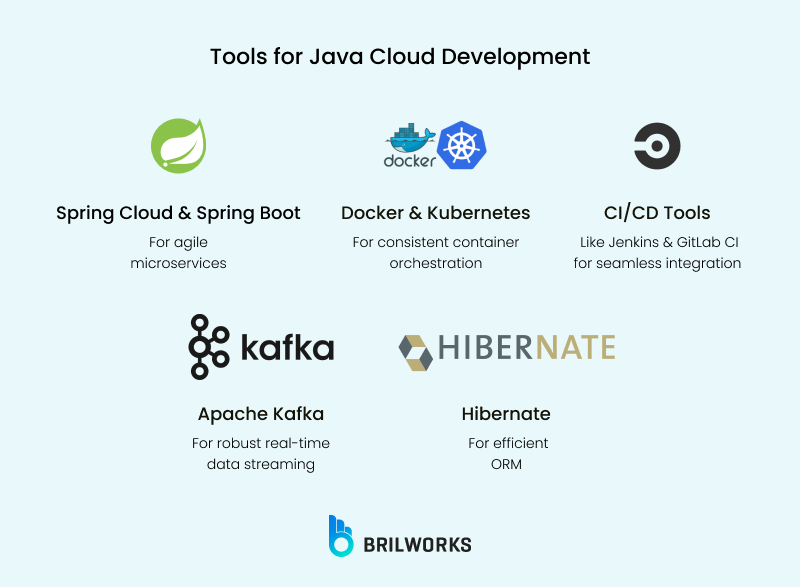
Spring Cloud is a powerful tool for developers to efficiently build cloud-scale applications. Its built-in features simplify the management of configuration and service discovery in a distributed system. Additionally, it automatically handles load balancing.
For example, an e-commerce platform with several services. You can build services such as inventory, payments, and user authentication on Spring Cloud. All of these services are deployed independently in the cloud.
Docker is a packaging tool. It ensures your code runs identically across development, testing, and production environments. Kubernetes is an orchestration platform. It automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Media and entertainment development companies use Docker to containerize Java-based microservices and Kubernetes to manage those containers across multiple cloud environments. This will ensure that the app can scale effortlessly based on user demand.
In 2011, Kafka was born as an open-source platform at LinkedIn to solve the low-latency issues. It has evolved into a more distributed event streaming platform. It is used for real-time data processing and microservice communication.
Hibernate is a Java framework that enables developers to easily map Java objects to relational database tables. By employing it, you can directly work with objects. Essentially, it takes away the complexities involved in data handling.
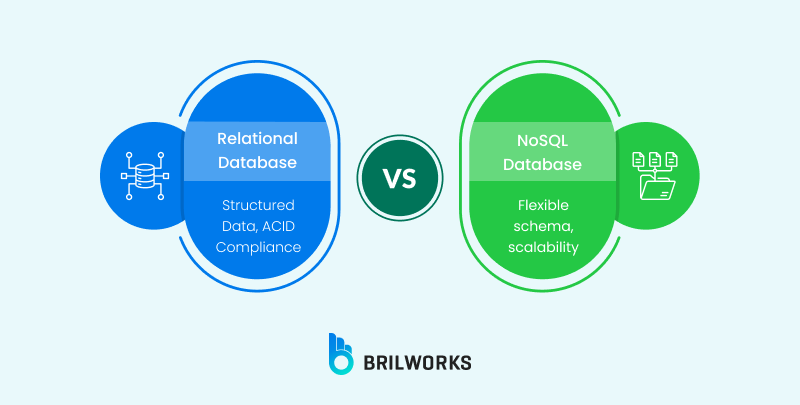
Databases come in different forms. When building scalable cloud applications, choosing the right database type is crucial. Relational databases, such as PostgreSQL and MySQL, are well-suited for organizing data. Select SQL databases for data integrity and complex query processing. If you need scalability and flexibility, especially for unstructured data, go for NoSQL.
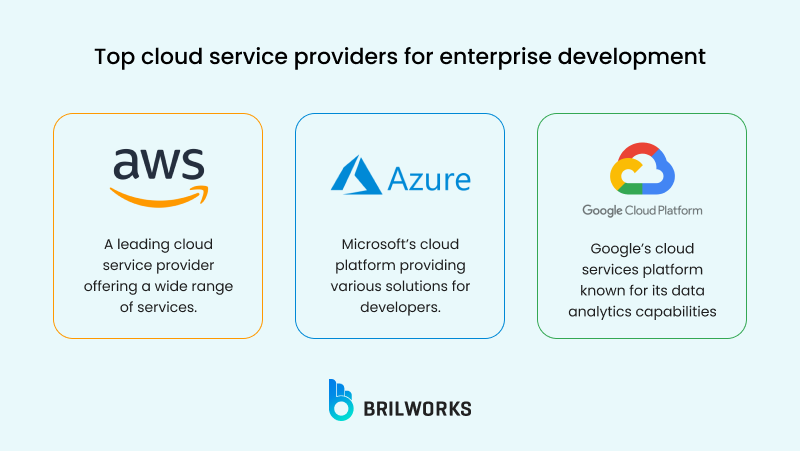
Cloud impacts your infrastructural scalability, cost, and performance. Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are the three most popular cloud service providers that offer custom cloud solutions, from compute power and storage to serverless services.
Continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD) are essential for maintaining the stability and scalability of your cloud applications. CI/CD tools, such as Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI, automate testing, building, and deployment procedures. These tools make releasing updates to cloud applications without downtime a whole lot easier. You can use popular CI/CD tools, including;
Jenkins: Automates testing and deployment, especially for Java-based microservices on Kubernetes.
GitLab CI: Integrates seamlessly with GitLab for efficient pipeline management.
CircleCI: Offers quick and flexible configurations for continuous delivery.
Effective monitoring and logging are vital for maintaining the health of your Java cloud application. Given the complexity of cloud-based systems, you may need tools to provide real-time visibility into application performance, uptime, and error monitoring.
80% of enterprise workloads are expected to be in the cloud by 2025.
Java is the second most-used language on AWS Lambda, proving its relevance in serverless computing.
Companies using Java cloud applications report 25-40% faster time-to-market due to robust frameworks and tools.
While building enterprise application security may be costly, it is too important a feature to eliminate. Though Java provides tools for enterprises. Developers can create a defense strategy. Let's explore some essential security practices to follow when building Java applications.
Avoid storing session data locally; use distributed caches like Redis for better scalability.
Implement OAuth2 for secure API communication and use Java’s built-in encryption libraries.
Auto-scaling and right-sizing instances can save you significant cloud expenses.
Use multi-region deployments and backups to ensure uptime even during outages.
Java continues to prove its mettle in the ever-evolving cloud landscape. Whether you’re building a new application or migrating to AWS, Java’s ecosystem offers unmatched support for creating scalable, high-performing solutions. To truly leverage this power, securing the right talent is key. Explore our "Strategic guide to hire Java developers" for an in-depth look at how to build your expert team.
Java has been a crucial ally in building business-oriented, high-performance applications over the past two decades. In this article, we'll examine how Java has evolved to accommodate today's modern cloud environment, including the trend toward serverless architecture. Java boasts an impressive, rich ecosystem that encompasses several powerful tools for building and deploying applications in the cloud.
And it's not just the tools. Java has a thriving community that constantly innovates to develop new features and updates, helping you stay ahead of the game. This has helped many Java development companies deliver cutting-edge applications for their clients. As an enterprise-grade Java development company, our team leverages the latest technologies to build and deploy compliant, top-shelf applications for our clients.
Java is ideal for cloud computing because of its platform independence, robust performance, and compatibility with the Java cloud hosting providers. It supports modern practices like containerization and distributed systems, which are essential for building scalable Java cloud applications.
Start by analyzing your existing Java application architecture to identify areas for optimization. Use AWS services like Elastic Beanstalk for easy deployment or AWS Lambda for serverless Java cloud programming. Refactor your code to align with Java cloud computing best practices, ensuring scalability and performance in the new environment.
Developers use Spring Cloud for the development of microservices, Hibernate for the management of database, and Eclipse MicroProfile for lightweight cloud application deployment. All these tools and Java programming for cloud computing will help in the streamlined development and scalability of Java cloud applications.
Choose your cloud Java hosting provider with aspects like compatibility with Java technologies, support for DevOps integration tools, scalability, and security. AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure platforms are well known to have optimized solutions for Java cloud computing and Java cloud applications.
Java programming for cloud computing offers dynamic scaling, secure processing, and supports the usage of advanced tools such as Docker and Kubernetes. The simplicity in building and managing efficient Java cloud applications through the ecosystem of libraries and frameworks is why many people choose Java for their cloud technologies.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements