COOPERATION MODEL
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
PRODUCT ENGINEERING
DevOps & Cloud
LOW-CODE/NO-CODE DEVELOPMENT
INDUSTRY
FRONTEND DEVELOPMENT
CLOUD DEVELOPMENT
MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT
LOW CODE/ NO CODE DEVELOPMENT
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES








From the latest V8 engine and improved test runner to better security with the Permission Model, Node.js 24 focuses on speed, stability, and modern APIs. This guide covers the most important Node.js 24 features, performance improvements, and release updates so you can decide when and how to upgrade.
Node.js 24 has arrived. For many developers, upgrades often feel incremental, but this release carries meaningful improvements that touch performance, security, and day-to-day coding experience. From a faster V8 engine to resource management improvements and security controls, Node.js 24 continues to close the gap between server-side JavaScript and what’s possible in modern browsers.
Whether you're maintaining an enterprise app or working with a node js consulting team to modernize your backend stack, these updates can streamline development and improve runtime efficiency. Let’s look at the release highlights, how they work in practice, and what they mean for your projects.
While the new V8 engine improves performance, legacy code might need optimization. Upgrading smoothly? Hire Node.js developers experienced in version migrations.
|
Feature |
Description |
Why It Matters |
|
V8 13.6 |
Faster performance and new JavaScript features |
Improves app speed and modern syntax support |
|
RegExp.escape() |
Built-in regex escaping |
Cleaner, safer pattern matching |
|
Float16Array |
Memory-efficient typed array |
Useful for ML, graphics, and memory-sensitive apps |
|
Permission Model |
Now stable (--permission) |
Stronger security and sandboxing |
|
URLPattern Global |
Native route matching |
Easier routing without regex |
|
npm v11 |
Faster installs, cleaner workflows |
Improves CI/CD reliability |
Every Node release includes a V8 upgrade, but version 13.6 brings real performance benefits. V8 optimizes JavaScript execution through just-in-time (JIT) compilation and efficient memory management, significantly boosting performance. Using Float16Array further reduces memory usage and improves data throughput, especially in performance-critical applications like graphics and machine learning.

For developers running compute-heavy workloads, this means faster response times without changing any code. If your application relies on older patterns, though, some performance adjustments may be needed. In those cases, hiring Node.js developers with migration expertise can save time during the upgrade.
Escaping strings for regular expressions has long been a source of bugs. Node.js 24 adds RegExp.escape(), a built-in utility that safely handles special characters.
Use case: If you’re building search filters, URL validators, or user-input-driven patterns, you no longer need custom helpers like escapeRegex(). It’s cleaner and more reliable out of the box.
Node.js 24 introduces Float16Array, a typed array for handling 16-bit floats. This reduces memory usage by half compared to Float32Array.
For developers working in graphics rendering, machine learning, or streaming large datasets, this makes applications more memory-efficient without major code changes.
A lower-level addition, Atomics.pause provides a way to pause execution in multi-threaded environments. This is especially useful for developers fine-tuning worker performance or dealing with synchronization issues in complex systems.
WebAssembly modules now support 64-bit memory addressing. If you’re compiling native libraries to run inside Node.js, this unlocks new possibilities for heavy workloads like image processing, game engines, or database operations.
A standout feature in Node.js 24 is support for Explicit Resource Management with await using.
await using file = await openFile('log.txt');// file is automatically released when out of scope
This ensures resources like file descriptors or sockets are closed automatically, reducing the risk of memory leaks. If you’ve ever forgotten to release a resource and seen the fallout in production, this feature will feel like a safety net.
Error.isError(obj) provides a consistent way to check for errors, even across different realms or libraries. It avoids the pitfalls of instanceof Error in complex codebases.
Security has become a defining theme of recent Node.js releases. The Permission Model, first introduced experimentally in Node.js 20, is now more stable with the CLI flag updated from --experimental-permission to --permission.
With this model, you can restrict your Node process from accessing files, environment variables, or networks it doesn’t need. For CLI tools, headless scripts, or untrusted environments, this is a powerful safeguard against supply chain vulnerabilities.
URLPattern, once limited to the browser, is now available globally in Node.js.

const pattern = new URLPattern({ pathname: '/user/:id' });
pattern.test('https://example.com/user/123'); // trueThis makes routing and URL parsing more straightforward. Framework authors, proxy developers, and crawler builders can now rely on a native API instead of juggling regex.
The built-in test runner no longer requires manual awaiting of subtests.
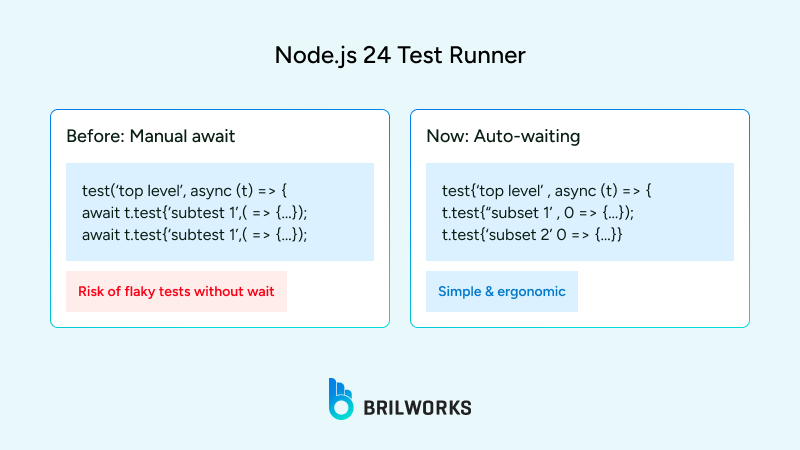
Before Node.js 24:
await t.test('subtest', async () => { ... });After Node.js 24:
t.test('subtest', () => { ... }); // Auto awaitedFor teams with large test suites, this reduces boilerplate and makes test files more concise.
Node’s HTTP stack continues to evolve with Undici 7.0, which improves spec compliance and smooths out developer experience when using fetch().
If your services rely heavily on APIs, proxies, or inter-service communication, these updates will make HTTP behavior more predictable.
The bundled package manager receives an upgrade too. npm v11 introduces:
Faster installs
Better lifecycle script control (--ignore-scripts fully enforced)
Removal of old npm hook command
Cleaner prompts in npm init
These changes may seem small, but they shave time off builds, reduce edge-case errors, and improve long-term stability.
As with any major release, Node.js 24 deprecates outdated APIs:
url.parse() → replace with the modern URL API
SlowBuffer, tls.createSecurePair, and some fs constants deprecated
Old constants like fs.F_OK being phased out
If you manage legacy codebases, it’s worth running a quick audit to plan updates before these APIs are removed in future releases.
Not every new feature will change your workflow today, but a few are worth adopting immediately:
Replace custom regex escaping with RegExp.escape.
Use await using for file or socket management to reduce leaks.
Try the Permission Model in smaller tools or services.
Refactor routes with URLPattern instead of regex.
Simplify test suites with the upgraded test runner.
Audit code for deprecated APIs and plan updates early.
Node.js 24 is not just another incremental release. Between performance upgrades, security enhancements, and developer conveniences, it pushes the ecosystem toward greater reliability and modern standards.
Whether you’re building high-performance backends, lightweight CLI tools, or complex applications, adopting these updates early will set you up for smoother development. And if your team is considering a move but unsure where to start, hire Node.js developers to help manage version migrations and safeguard production code.
Node.js 24 introduces several developer-focused updates, including the V8 13.6 engine for better performance, RegExp.escape() for safer regex handling, Float16Array for memory efficiency, the Permission Model with a stable --permission flag, global availability of URLPattern, and an upgraded test runner. It also bundles npm v11 and Undici 7.0, along with deprecations of older APIs like url.parse().
The biggest performance gain comes from the upgrade to the V8 13.6 engine, which optimizes JavaScript execution speed and adds support for new language features. Memory-sensitive applications also benefit from Float16Array, which uses half the memory of Float32Array. Together, these changes make Node.js 24 faster and more resource-efficient.
Beyond performance upgrades, Node.js 24 stabilizes the Permission Model (moving from --experimental-permission to --permission), introduces deterministic cleanup with await using, and improves compatibility with web standards by making URLPattern global. Compared to earlier releases, it also advances built-in testing and ships with updated tooling like npm v11 and Undici 7.0.
If you rely on long-term support (LTS) releases, you may prefer to wait until Node.js 24 transitions to LTS. However, for teams eager to adopt new features, migrating now can be beneficial. Running an audit of deprecated APIs is recommended before upgrading.
The Permission Model allows developers to sandbox Node.js applications by restricting access to resources like the filesystem, network, or environment variables. For example, a script can be run with no network permissions, reducing the risk of supply chain attacks. The feature is more stable in Node.js 24, with the new --permission flag.
Node.js 24 comes with npm v11, which improves installation speed, adds better lifecycle script control, removes outdated commands, and streamlines project initialization. This update enhances developer workflows, especially in CI/CD pipelines.
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements
Get In Touch
Contact us for your software development requirements